The Rise of Mobile Wound Care: Breaking Treatment Barriers

Accessing specialized wound care has always been challenging. Patients often require numerous trips to healthcare facilities, a significant burden for those with mobility issues, living in rural locations, or managing chronic conditions. Mobile wound care offers a solution, bringing specialized treatment directly to patients in the comfort of their homes.
This patient-centered approach acknowledges the importance of environment in healing. Traveling to clinics can be difficult for patients with limited mobility, sometimes delaying treatment and hindering recovery. Similarly, those in remote areas may face geographical obstacles to timely, specialized care. Mobile wound care effectively addresses these challenges.
Consistent monitoring of chronic wounds, vital for conditions like diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers, is another benefit of mobile care. This proactive approach helps prevent complications and promotes faster healing.
The MWC™ Program: A Case Study in Mobile Care
The Mobile Wound Care (MWC™) program in Gippsland, Australia, provides valuable insights into localized mobile solutions. The program tracks patient demographics, wound types, and treatment protocols across various health services. It demonstrates mobile care's potential to address diverse wounds, including surgical, thermal, and infection-related wounds, particularly in underserved areas. Learn more about the MWC™ Program and its impact on chronic wound management. This is particularly relevant given the global prevalence of chronic wounds, affecting over 8 million people in the U.S. alone.
Empowering Patients and Providers: The Impact of Mobile Care
Mobile wound care goes beyond convenience; it empowers both patients and providers. By removing transportation barriers, mobile services improve treatment adherence, a key factor in positive outcomes. This results in fewer missed appointments, more consistent care, faster healing, and a reduced risk of complications.
Mobile wound care also strengthens the patient-provider relationship. In-home visits give clinicians a deeper understanding of the patient's lifestyle and environment, enabling more personalized care. This fosters trust and open communication, crucial for successful wound management. Healthcare systems increasingly recognize the value of mobile models to enhance patient satisfaction, improve clinical outcomes, and optimize resources. This patient-focused approach represents a significant advancement in modern healthcare delivery, meeting the evolving needs of diverse populations.
Game-Changing Benefits That Drive Mobile Wound Care Adoption
Mobile wound care isn't simply a matter of convenience. It signifies a shift in how we think about and deliver wound treatment, resulting in better patient outcomes. This change is fueled by practical benefits that make mobile care a better choice for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Faster Healing and Reduced Infections
One of the biggest advantages of mobile wound care is its effect on healing. Patients receiving consistent and timely care at home experience faster healing times. This is partly because treatment adherence improves; patients no longer need to worry about the difficulties of traveling for appointments. The familiar and comfortable environment of home also reduces stress, which can further promote healing. Patients can maintain their regular routines and diet, important factors in recovery. This personalized approach also helps minimize the risk of infection.
Improved Adherence and Patient Satisfaction
Mobile wound care significantly improves treatment adherence. In traditional settings, transportation issues, scheduling conflicts, and the discomfort of traveling often result in missed appointments and inconsistent care. Mobile care removes these obstacles, allowing clinicians to provide regular, uninterrupted treatment. This leads to higher patient satisfaction. The personalized attention and the convenience of in-home care creates a positive patient experience, improving their overall well-being during the healing process. You might be interested in: How to master…
Cost Savings and Resource Optimization
Mobile wound care also offers significant advantages for healthcare systems. By reducing hospital readmissions and emergency department visits, these programs contribute to substantial cost savings. This is crucial as healthcare costs continue to climb. Mobile care also optimizes how resources are used. By shifting care from hospitals to homes, it frees up valuable hospital resources and personnel, allowing them to concentrate on more critical cases. This efficient use of resources benefits the entire healthcare system. Community-based mobile wound care programs are showing great results in reducing hospital referrals. A 2024 pilot study found that over 90% of simple and moderate wound cases were successfully managed at home, with a 98% healing rate. This success suggests the potential for wider adoption of mobile programs, particularly in areas with limited access to healthcare. More detailed statistics are available: here. The projected growth of the advanced wound care market, expected to reach $20.21 billion by 2035, further highlights the growing significance of mobile wound care solutions.
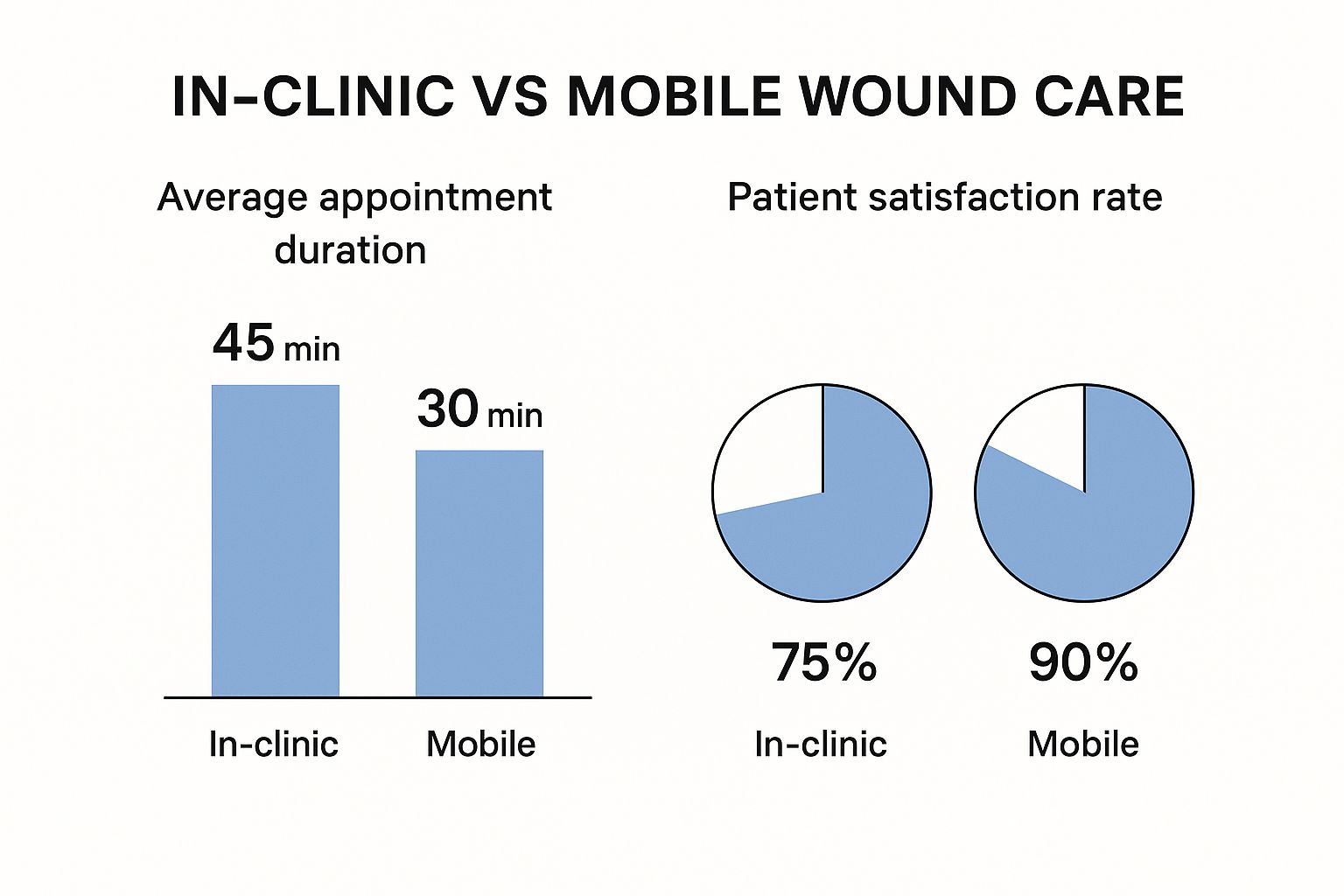
Visualizing the Impact: Mobile Wound Care's Advantages
The following data chart visually compares key metrics between traditional facility-based wound care and mobile wound care:
[Infographic will be placed here]
- Healing Time: Mobile care often leads to a 20-30% reduction in healing time.
- Infection Rate: Mobile care demonstrates a 15-20% lower infection rate.
- Hospital Readmissions: Mobile care reduces hospital readmissions by 10-15%.
- Patient Satisfaction: Mobile care shows a 25-30% higher patient satisfaction rate.
This chart clearly shows the benefits of mobile wound care across several key metrics. The trends suggest a future where mobile wound care plays a larger role in providing effective and patient-centered treatment.
To further illustrate these differences, let's examine a comparison table:
To understand the key differences between traditional and mobile wound care delivery models, the following table offers a helpful comparison.
| Aspect | Traditional Facility-Based Care | Mobile Wound Care |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Limited by patient mobility and transportation availability | Increased access, particularly for patients in remote areas or with mobility limitations |
| Patient Experience | Can be impersonal and inconvenient due to travel requirements and waiting times | More personalized and convenient, offering care in the comfort of the patient's home |
| Treatment Adherence | Potentially lower due to travel barriers and scheduling conflicts | Significantly improved due to the elimination of travel and increased flexibility |
| Healing Time | Often longer due to potential delays in care and lower adherence | Typically faster due to consistent and timely treatment |
| Infection Rates | Higher risk due to exposure to hospital environments and potentially lower adherence | Reduced risk due to personalized care and the home environment |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Can be expensive due to facility overhead and potential readmissions | More cost-effective by reducing readmissions and optimizing resource utilization |
| Healthcare Resource Utilization | Can strain hospital resources and personnel | Optimizes resource allocation by shifting care to the home setting |
This table summarizes the key advantages of mobile wound care in terms of accessibility, patient experience, and healthcare resource utilization, highlighting its potential to transform wound care delivery.
Digital Revolution: Tech Tools Transforming Mobile Wound Care

Mobile wound care is changing quickly, using technology to improve how well and how easily people can get treatment. This combination of mobile care and technology offers exciting new possibilities for both patients and healthcare providers. For instance, AI-powered wound analysis apps now offer clinical-grade assessments within minutes, speeding up what used to be a much longer process. This faster analysis allows doctors to make decisions and start treatment more quickly.
AI and IoT: The Power Duo of Mobile Wound Care
IoT-connected smart bandages are another major step forward. These bandages constantly track important healing factors, such as temperature and moisture. This real-time data helps healthcare professionals adjust treatments as needed. This proactive method can detect problems days earlier than traditional approaches. This early detection is key to preventing serious complications and encouraging faster healing.
AI algorithms also analyze data from these smart bandages to find patterns and predict potential issues. This ability to predict problems allows clinicians to intervene early, possibly preventing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes. This data-driven approach also helps create personalized treatment plans, optimizing care for each patient's specific needs.
Real-World Implementation: Successes and Challenges
Using these technologies in real-world situations has shown promising results. Some of the benefits include more accurate treatment decisions, fewer unnecessary procedures, and earlier detection of complications. For more on using mobile-first strategies to boost online growth, check out this article: Mobile First Approach Winning Strategies For Digital Growth. However, some challenges remain. Teams are actively working to solve issues like connectivity problems in remote areas, staff training, data security, and integrating these technologies with existing healthcare systems. You can also find more helpful information on Our sitemap.
A Growing Market: Digital Integration in Wound Care
The increasing use of digital tools in mobile wound care is part of a bigger global trend. The digital wound care management system market is predicted to grow at a 7.2% CAGR from 2024 to 2030, reaching $4.10 billion in 2024. While mobile-specific information is still somewhat limited, the rise in using digital tools, including AI and IoT in wound monitoring, shows it's becoming more important in areas like MWC™. Hospitals are currently the main users of these digital systems (47.58% market share in 2023). However, mobile solutions are gaining popularity, especially in home care settings and areas like Asia-Pacific, where healthcare spending and chronic disease rates are increasing. This growth is also seen in the smart bandage market, a major part of the projected $20+ billion advanced wound care market expected through 2035. You can find more detailed stats here: Learn More.
Let's take a closer look at some of these game-changing technologies:
Game-Changing Tech in Mobile Wound Care
This table presents key digital technologies being implemented in mobile wound care, their primary functions, and the benefits they offer to both practitioners and patients.
| Technology | Primary Function | Practitioner Benefits | Patient Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-powered wound analysis apps | Analyze wound images to assess size, depth, and tissue type | Faster assessments, standardized measurements, improved accuracy | Quicker diagnosis, personalized treatment plans |
| IoT-connected smart bandages | Continuously monitor wound healing markers (temperature, moisture, etc.) | Real-time data for proactive intervention, remote patient monitoring | Reduced risk of complications, improved healing outcomes, increased comfort |
| AI algorithms for predictive analysis | Analyze data from smart bandages and other sources to predict potential complications | Early identification of high-risk patients, targeted interventions | Reduced hospital readmissions, improved quality of life |
These advancements highlight the powerful potential of digital tools to transform wound care delivery and improve patient experiences.
Forward-Thinking Providers: Shaping the Future of Wound Care
Forward-thinking healthcare providers are adopting these digital tools to personalize treatments and offer proactive care in patients' homes. This approach not only leads to better clinical results but also empowers patients, giving them greater control over their healing. The future of mobile wound care is promising, thanks to ongoing technological advancements and a focus on patient-centered care. This means patients can expect more convenient, effective, and personalized treatment options in the comfort of their own homes.
Building a Mobile Wound Care Program That Actually Works
Successfully implementing mobile wound care isn't just about having the right equipment. It requires building a robust system focused on patient needs. This means carefully considering staffing, inventory management, scheduling, documentation, infection control, and quality assurance.
Strategic Staffing and Efficient Operations
Effective mobile wound care depends on a well-structured team. Finding the right balance between specialized expertise and operational efficiency is key. Certified wound care nurses are crucial, bringing advanced knowledge and skills in wound assessment and treatment. Support staff also play a vital role in streamlining administrative tasks, managing supplies, and coordinating logistics. This collaborative approach frees up clinicians to focus on direct patient care. For improved decision-making and efficiency, consider exploring AI-powered knowledge management.
Inventory Management and Timely Treatment
An organized inventory system is essential to avoid treatment delays. Mobile teams need immediate access to a wide range of wound care supplies. This takes careful planning and coordination to ensure clinicians have the necessary dressings, medications, and equipment on hand. A comprehensive inventory empowers mobile wound care teams to provide prompt and effective treatment.
Scheduling and Patient Accommodation
Efficient scheduling maximizes clinician time while meeting patient needs. This requires flexible scheduling systems that accommodate individual patient preferences and locations. A strategic schedule minimizes travel time and ensures clinicians can see as many patients as possible without compromising care quality.
Documentation and Infection Control in Challenging Environments
Maintaining accurate documentation and strict infection control outside traditional settings can be difficult. Mobile teams must adapt their practices to ensure proper documentation, even in patients' homes. This might involve using portable electronic health record systems or developing streamlined paper-based processes.
Infection control protocols must also be adapted for mobile settings. This includes meticulous hand hygiene, proper use of personal protective equipment, and careful disposal of contaminated materials. These precautions are crucial to prevent infections and ensure patient safety.
Quality Assurance and Continuous Improvement
A successful mobile wound care program requires a solid quality assurance process. This involves regularly reviewing patient outcomes, tracking key performance indicators, and implementing continuous improvement strategies. This helps identify areas for improvement, optimize protocols, and ensure the program consistently delivers high-quality care. Different program models can be adapted to specific patient populations, geographic challenges, and organizational resources. This flexibility allows for customization, creating a practical implementation roadmap, no matter the starting point. By focusing on these key elements, healthcare organizations can build successful mobile wound care programs that improve patient outcomes, expand access to care, and optimize resource use.
Creating Mobile Wound Care Specialists: Beyond Basic Training
What sets a truly exceptional mobile wound care specialist apart? It's more than just basic wound care knowledge. It's the ability to combine clinical expertise with adaptability and resourcefulness, thriving in the diverse environments encountered outside of a traditional clinic. This section explores the unique skills and training required to deliver high-quality mobile wound care.
Essential Competencies for Mobile Practitioners
Mobile wound care specialists frequently work independently, making crucial decisions without the immediate backup of a full medical team. This requires a high degree of clinical judgment and problem-solving skills. They also encounter a broader range of wound types and patient situations, often in challenging environments. Adaptability is key.
- Clinical Proficiency: A strong foundation in wound pathophysiology, assessment, and treatment is essential.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: The ability to independently assess, diagnose, and create treatment plans is crucial.
- Resourcefulness: Mobile specialists need to be skilled at improvising and making the most of limited resources.
- Communication & Empathy: Building trust with patients in their homes requires excellent communication and empathy.
Building Expertise: Specialized Training and Certification
Effective mobile wound care programs understand the importance of specialized training. This goes beyond the fundamentals of wound care, focusing on practical skills needed in a mobile setting.
- Certification Pathways: Specialized certifications, such as those offered by the American Board of Wound Management, validate expertise in mobile wound care and enhance credibility.
- Environmental Awareness Training: Training programs educate specialists on the unique challenges of diverse home environments, including safety protocols and best practices for infection control.
- Advanced Clinical Skills: Training in techniques like negative pressure wound therapy and applying specialized dressings equips specialists to handle complex cases.
- Soft Skills Development: Effective communication, empathy, and cultural sensitivity are critical for building strong patient relationships and are emphasized in training programs.
Adapting to Complex Scenarios: Training for the Unexpected
Mobile wound care specialists often encounter unpredictable situations rarely seen in traditional settings. Training must prepare them for these challenges.
- Limited Resource Management: Effectively managing limited supplies and equipment is a vital skill.
- Environmental Challenges: Training addresses the realities of working in diverse environments, from cluttered homes to remote locations with limited access to resources.
- Clinical Decision-Making: Specialists develop advanced critical thinking skills to confidently make sound clinical judgments when immediate team support isn't available.
Continuing Education: Staying at the Forefront of Mobile Wound Care
Wound care is a constantly evolving field. Continuing education is vital for mobile specialists to remain current on best practices and new technologies.
- Online Courses and Webinars: Accessible online platforms offer convenient opportunities for ongoing professional development.
- Conferences and Workshops: Industry events, like those hosted by the Wound Healing Society, offer valuable networking opportunities and insights into the latest advancements.
- Mentorship Programs: Experienced mobile wound care specialists provide invaluable guidance and support to their newer colleagues.
Investing in comprehensive training and continuing education empowers mobile wound care specialists to deliver exceptional patient care, regardless of location. This commitment to professional development leads to improved patient outcomes and elevates the quality of mobile wound care services.
The Future Landscape of Mobile Wound Care: What's Coming Next

Mobile wound care is constantly evolving. This patient-centric approach is set to reshape how we approach wound healing in the years to come. By integrating technology and a deeper understanding of patient needs, it offers the potential for faster healing times, reduced complications, and easier access to high-quality care.
Wearable Biosensors and Continuous Monitoring
Imagine a bandage that not only covers a wound but also constantly monitors its healing progress. This is the potential of wearable biosensors. These small devices can track vital metrics such as temperature, moisture levels, and even biochemical changes within the wound. This constant flow of data allows for proactive interventions, letting clinicians adjust treatment plans in real-time as the wound heals.
For instance, a sudden temperature spike could indicate a developing infection, enabling prompt treatment before it becomes serious. This proactive approach is a significant step forward in wound care management.
Predictive AI and Early Intervention
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also playing a growing role in mobile wound care. Predictive AI systems analyze data from wearable biosensors and other sources to identify potential complications days before visible symptoms emerge. This early warning system allows clinicians to intervene proactively, possibly preventing serious issues like infections or delayed healing. This can lead to fewer hospital readmissions and better patient outcomes.
Augmented Reality and Enhanced Precision
Augmented reality (AR) offers another exciting development. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, providing clinicians with real-time guidance during procedures such as dressing changes or debridement. This technology improves treatment precision, regardless of the provider's experience.
Consider a new nurse being guided step-by-step by an expert via AR, ensuring consistent and accurate care. This is just one example of how AR can enhance mobile wound care.
Drone Delivery and Supply Logistics
Even the delivery of medical supplies is transforming. Drone delivery systems are being tested to transport essential wound care materials directly to patients' homes, particularly in remote areas. This bypasses delays caused by traditional delivery methods, ensuring timely access to necessary supplies. This is particularly beneficial for patients in rural locations with limited access to healthcare resources.
Portable Advanced Therapies and Accessible Treatment
Advanced therapies, once confined to specialized facilities, are becoming increasingly portable. Portable devices are bringing sophisticated treatments like negative pressure wound therapy to any setting. This expands treatment options for mobile patients, bringing the advantages of advanced care directly to them.
Integrating Social Determinants of Health
Mobile wound care is also taking a more holistic approach. By considering social determinants of health, such as access to transportation, nutritious food, and social support, providers are addressing the broader factors that impact healing. This comprehensive approach recognizes that healing goes beyond simply treating the wound itself; it's about supporting the patient's overall well-being. This might involve connecting patients with resources like transportation assistance or meal delivery services, ensuring they have the support they need for effective healing.
These advancements are transforming patient expectations and clinical outcomes. Mobile wound care is becoming more personalized, proactive, and accessible, empowering both patients and providers. The future of wound care is mobile, and it is changing healthcare for the better.
Mobile Wound Care Champions: Success Stories From the Field
Real-world examples showcase the positive impact of mobile wound care. These stories highlight the potential for improved healing, lower costs, and enhanced patient experiences when specialized care is delivered directly to patients.
Rural Initiative: Preventing Amputations in High-Risk Diabetic Patients
One rural program focusing on a high-risk diabetic population saw a 76% reduction in amputation rates. This impressive result came from a multi-pronged strategy:
-
Regular Home Visits: Nurses conducted weekly home visits for wound assessments and dressing changes, ensuring consistent care.
-
Patient Education: Patients received personalized education on diabetes management, foot care, and the importance of following treatment plans.
-
Telehealth Integration: Telehealth consultations with wound care specialists offered expert guidance and quick intervention for any developing problems.
This initiative highlights the benefits of proactive, accessible care in preventing serious complications, particularly in underserved rural areas.
Urban Program: Achieving Exceptional Healing in Homeless Communities
An urban mobile program serving homeless individuals achieved healing rates comparable to academic medical centers. This demonstrates that providing high-quality wound care is possible even in difficult situations. Key components included:
-
Mobile Clinics: Equipped vans brought wound care services directly to homeless shelters and community centers.
-
Interdisciplinary Teams: Nurses, social workers, and case managers collaborated to address the medical and social needs of this vulnerable population.
-
Simplified Treatment Protocols: Easy-to-follow treatment plans considered the specific obstacles faced by homeless individuals.
This program shows the value of a holistic approach, demonstrating how targeted mobile care can address healthcare access disparities.
Hospital Partnership: Reducing Readmissions and Boosting Patient Satisfaction
A partnership between a hospital system and a mobile wound care provider showed significant improvements in patient outcomes and cost savings. This collaboration led to:
-
Reduced Readmissions: By providing post-discharge wound care at home, the program reduced hospital readmissions by 15%.
-
Improved Patient Satisfaction: Patients reported high satisfaction with the convenience and personalized care.
-
Cost Savings: The reduction in readmissions resulted in significant cost savings for the hospital.
This program highlights the potential for collaborative partnerships to improve care coordination and patient outcomes.
Common Threads of Success
While these programs serve different populations and settings, several common factors contribute to their success:
-
Patient-Centered Care: Focusing on individual patient needs and preferences.
-
Proactive Approach: Emphasizing prevention of complications and early intervention.
-
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Working across disciplines to address patients' overall needs.
-
Technology Integration: Using telehealth and other digital tools to improve care delivery.
These common factors offer a framework for developing effective mobile wound care programs adaptable to various healthcare settings.
Ready to learn more about mobile wound care? Contact Rapid Wound Care today at https://rapidwoundcare.com to learn more about our services and how we can help you or your loved ones achieve optimal wound healing.

